Crypto staking vs crypto lending – at first glance, crypto staking and crypto lending seem like basically the same thing. You lock up your crypto on a platform and earn yield. In this article, we compare the crypto two products and highlight a range of differences in terms of their risk profiles, returns and viability.
What Is Crypto Lending?
Cryptocurrency lending is a financial service that allows crypto holders to lend popular cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and stablecoins to borrowers in exchange for interest or ‘yield’.
Typically, lenders don’t interact with borrowers directly, instead, they provide their funds to centralized online platforms like Youhodler and Nexo, or Defi protocols like CREAM or AVE which, in turn, lend these assets out to individual and institutional borrowers. The interest rates paid to lenders vary depending on the current market demand for the tokens being lent and their overall liquidity. Stablecoins such as Tether and USDC usually provide the highest interest rates.
In simple terms, the ‘process’ being applied is the same as that seen in traditional banking for hundreds of years. Lenders send their funds to a bank for a conservative return. The bank then uses those funds to issue loans at a higher interest rate to borrowers. They, in turn, pay back the loans and the bank keeps a percentage and pays modest interest to its lenders.
What Is Crypto Staking?
Crypto staking refers to the process of holding and “staking” a particular cryptocurrency in a digital wallet to support the operations of a blockchain network. In return for staking their coins, participants can earn additional cryptocurrency as a reward.
Staking differs from crypto lending in that the staked crypto is not lent out to borrowers. In a proof-of-stake blockchain, new blocks are not mined like in a proof-of-work (PoW) system (e.g., Bitcoin and Litecoin). Instead, the process of block creation and validation is carried out by validators who are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they have staked and other factors, such as their reputation or random selection algorithms. Bitcoin and other proof-of-work coins cannot be staked.
Here’s how crypto staking generally works: Crypto holders who want to participate in the network’s block validation process can “stake” or lock up a certain amount of their coins as collateral. Popular token choices for crypto staking include Ethereum, Solana, Avalanche, Polkadot, and Cardano.
By staking their coins, users signal their commitment to maintaining the network’s security and follow the rules of the protocol. Terms to understand include;
- Block Validation: Validators are chosen to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they have staked. In some PoS systems, the probability of being selected as a validator is proportional to the number of coins staked (e.g., if you stake 5% of the total coins, you have a 5% chance of being chosen).
- Consensus: Validators propose and validate new blocks, and consensus is achieved among them. In many PoS systems, validators are required to deposit a security deposit (often referred to as a “bond”) to prevent malicious behavior. If a validator is found to be acting dishonestly or against the rules, their staked coins can be slashed, meaning a portion of their stake is taken away as a penalty.
- Rewards: Validators who successfully validate transactions and create new blocks are rewarded with additional cryptocurrency tokens as an incentive for securing the network. These rewards are often distributed proportionally based on the amount of coins staked.
- Governance: Some PoS systems also allow stakers to participate in on-chain governance by voting on proposed protocol upgrades and changes. This gives stakers a say in the future direction of the blockchain network.
Staking offers several benefits, including the potential for earning passive income through block rewards, participating in network governance, and contributing to the security and decentralization of the blockchain network.
How Do The Risk Factors Of Crypto Staking And Lending Compare?
Crypto Lending Risk Factors
Sadly, the risks of crypto lending, particularly in the case of centralized platforms, are nothing less than extreme. Since mid-2022 the Celsius, Hodlnaut, Vauld, Gemini Earn, LendingBlock, BlockFi, Midas Investments, Inlock, MyConstant, and most recently Coinloan, platforms have all ceased operations while holding millions in customer deposits.
Most of them have declared bankruptcy and it will likely be years before investors see any funds returned. And it’s here that the analogy with traditional banking falls apart. Whereas depositor funds in the U.S are protected in the case of bank failure by the FDIC insurance scheme (and by similar schemes in most other countries), there is no insurance scheme for crypto deposits.
While there are a range of other risks related to crypto lending such as hacking, security breaches, government intervention and founder ‘rug pulls’, platform failure through gross mismanagement is by far the greatest risk – and has been behind almost all the centralized lending platform failures to date. Bottom line? Crypto lending where the lending platform holds the private keys to a user’s funds is extremely high risk.
Crypto Staking Risk Factors
The risk profile of staking cryptocurrency is less extreme than crypto lending, with most risk factors relating to price volatility. The value of your staked tokens can fluctuate significantly, which means you will be exposed to potential losses if your crypto’s price drops while your tokens are staked. Other risks include;
- Network Risk: Staking usually involves participating in the consensus mechanism of a blockchain network. If the network experiences technical issues, such as a 51% attack or a software bug, your staked tokens could be at risk. In such situations, you could temporarily lose access to your staked tokens or even face permanent loss.
- Slashing Risk: Some staking protocols have mechanisms in place to penalize validators or stakers for malicious behavior or network rule violations. If you fail to follow the rules or act inappropriately, a portion of your staked tokens may be confiscated or “slashed.”
- Regulatory Risk: Regulatory changes or crackdowns on cryptocurrencies and staking activities can affect the legal landscape and potentially impact your ability to stake or the value of your staked tokens.
- Counterparty Risk: Depending on the staking mechanism, you might need to delegate your tokens to a third-party validator or staking pool. This introduces counterparty risk, as you’re trusting another entity with your funds (as with lending platforms). If the validator or staking pool is compromised or acts dishonestly, your staked tokens will be at risk. It is possible to reduce custody risk with solo staking, where instead of delegating your crypto to a validator node or a staking pool you maintain control of your assets, instead of entrusting them to a third party.
- Inflation Risk: Some staking networks have inflationary token models where new tokens are minted and distributed as rewards to stakers. If the rate of inflation is high, it can dilute the value of your staked tokens over time, potentially reducing your overall returns. For example, here is the estimated current inflation rate of the most popular staking tokens.
Ethereum – 0.52% (post merge, previously – 4.2%)
Cardano – 4.72%
Solana – 6.02%
Avalanche – Highly variable – has been as high as 40%
Polkadot – 6-10% on average
It’s worth pointing out that if you’re lending any of these tokens to platforms like Nexo or Youholder, the same inflation risk applies. For example, the current interest rate for lending Solana to Nexo is 8%, and to Crypto.com, 3%. - Technology Risk: Staking typically requires the use of specialized software wallets, smart contracts, or staking platforms. If these technologies have vulnerabilities or are not properly secured, your staked tokens could be exposed to hacking, theft, or loss.
Crypto Staking Or Lending – which has the highest returns?
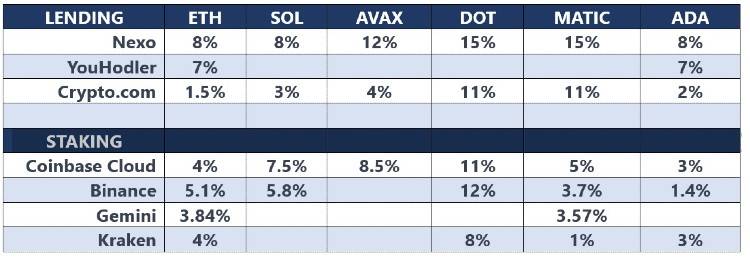
In the chart below we have recorded the current claimed yield for a number of popular tokens, both in terms of lending and staking, on a range of the largest platforms. From this small sample, it is evident that there is little difference between the annual returns from staking or lending – particularly when one considers the annual inflation rate of many tokens, and in the case of many of the staking platforms, the fees charged. Check here for current staking rates.
Conclusion
As explained above, crypto staking and crypto lending are two different things. Only proof-of-stake cryptocurrencies can be staked so you cannot stake Bitcoin, Litecoin or any other proof-of-work token (platforms that offer Bitcoin ‘staking’ are misusing the word). In terms of return on investment, the current rates on offer from staking and lending are quite similar. In addition, both processes have similar risk profiles, although if we had to choose which one is less risky our vote would be for staking – as the carnage in the crypto lending space in the last year has been spectacular.
That said, exchange collapses are possible (FTX offered a lot of staking, for example), so we recommend staking on well-established, well-managed platforms only. It’s also worth noting something that Binance says in its staking FAQs – where it stresses that stakers shouldn’t even think about staking from an ‘investment’ perspective.
“It is important to clarify an important misconception and note that staking is first and foremost, not a rewards mechanism or investment scheme, but a consensus model designed to contribute to the security, stability, and participation of blockchain networks.
While blockchain networks generate rewards in order to incentivize asset holders to participate in this process, staking should not be interpreted as an investment. Instead, it should be interpreted as a way for asset holders to participate in securing the blockchain and helping to validate transactions.”
There! What were you thinking trying to get a return on your token investments? You should be staking because you love your blockchains, not for money! Lesson learned.