Top 5 Growth Sectors for Entrepreneurs
8.7 min read
Updated: Dec 20, 2025 - 08:12:16
Entering 2026, founders face a market where AI-driven productivity, aging demographics, and energy constraints are reshaping which startups can scale profitably. The five sectors with durable demand, proven revenue models, and realistic near-term ROI, helping entrepreneurs target opportunities where customer budgets are already allocated and infrastructure is in place.
- AI & Intelligent Automation: Enterprise adoption is accelerating (29% using, 44% adding within a year), creating demand for industry-specific automation, supply-chain optimization, predictive maintenance, and compliance tools, especially where ROI is measurable within months.
- Sustainable & Energy-Efficient Tech: AI-driven energy consumption is pushing businesses to adopt efficiency and management tools; opportunities center on optimization, storage, and automation rather than capital-heavy generation.
- Health, Wellness & Preventive Tech: Personalized medicine (projected to $206B by 2033) and mental-wellness platforms create strong entry points for niche diagnostics, digital therapeutics, and subscription-based preventive solutions.
- Digital & Immersive Experiences: Practical AR/VR for retail, training, and education, paired with generative AI content production, offers scalable B2B service models that enhance existing workflows rather than building new platforms.
- Subscription, On-Demand & Platform Services: Recurring-revenue models, embedded fintech tools, and vertical marketplaces remain attractive due to predictable cash flow and strong unit economics, especially in fragmented industries with supply frictions.
The entrepreneurial landscape entering 2026 bears little resemblance to previous startup eras. AI is projected to contribute up to $15.7 trillion to global GDP by 2030, with each dollar spent on business-related AI generating $4.6 in economic value. Yet this statistic only hints at the broader transformation reshaping which sectors offer genuine opportunity versus those facing disruption. For founders planning launches in 2026, understanding where growth concentrates makes the difference between riding powerful tailwinds and fighting headwinds that no amount of execution can overcome.
The data reveals five sectors demonstrating sustained momentum, supported infrastructure, and clear customer demand. These aren’t speculative bets on distant futures, they represent markets with established revenue models, proven customer acquisition channels, and realistic paths to profitability within typical venture timelines.
AI and Intelligent Automation Services
The enterprise agentic AI market is expected to reach $24.50 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 46.2%, but the real opportunity lies beyond chatbots and content generation. Currently 29% of firms already use agentic AI, while 44% plan to adopt within a year, creating immediate demand for implementation services, custom solutions, and industry-specific applications.
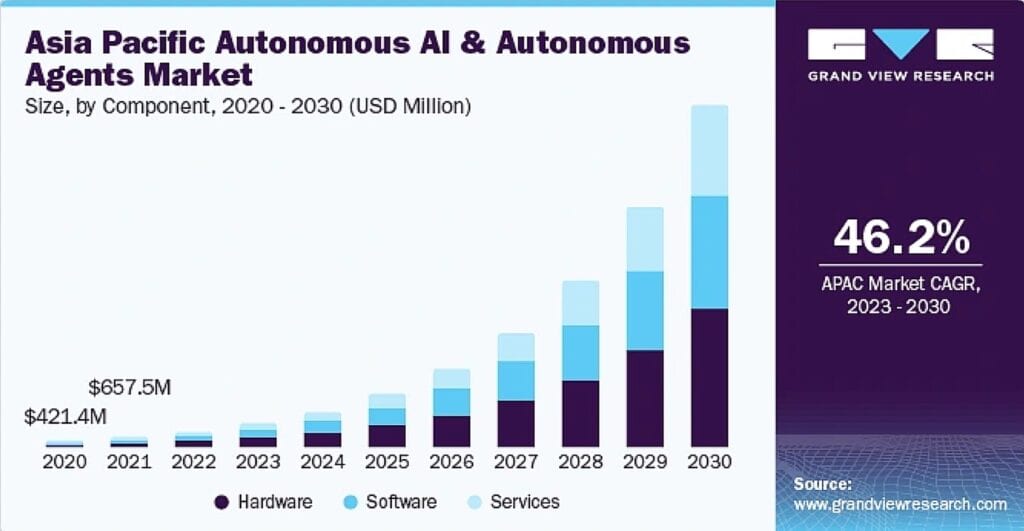
Source: Grand View Research
The sector’s evolution reflects a shift from experimentation to integration. Industries most exposed to AI record approximately 3x faster revenue growth per employee and double the wage growth, while workers with AI-related skills earn a 56% wage premium. This premium signals genuine productivity gains rather than hype, validating AI as infrastructure rather than novelty.
Entrepreneurs should focus on vertical applications where AI solves specific, high-value problems. The global healthcare automation market is projected to grow from $38.6 billion in 2023 to $94 billion by 2033 at a 9.3% CAGR, driven by chronic labor shortages and rising operational costs. Service businesses offering installation, maintenance, and customization for robotics systems can generate revenue while avoiding the capital intensity of hardware manufacturing.
The challenge involves managing expectations. More than 40% of current agentic AI projects are expected to be discontinued by 2027 because of escalating costs and unclear returns on investment. Successful ventures will demonstrate measurable ROI quickly rather than promising distant transformation. The global AI market was $87.27 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $647.6 billion by 2030, but winners will serve pragmatic customers seeking efficiency gains, not enterprises chasing science fiction.
Opportunity areas include AI-powered supply chain optimization (reducing costs by 20-30% according to industry estimates), predictive maintenance systems, and compliance automation. Small businesses in the IT field can help clients build specialized platforms like AI-driven analytics for specific industries or compliance-focused SaaS products, serving markets underserved by generalist AI vendors.
Sustainable and Green Technologies
Clean energy is becoming central to the global economy, with solar, wind, green hydrogen, and energy storage leading power production by 2026. Unlike previous cleantech waves that relied on subsidies and green premiums, current opportunities rest on commercial viability and cost competitiveness.
The adoption of SiC and GaN in data center power systems is predicted to reach 17% by 2026 and exceed 30% by 2030, driven by AI’s voracious energy demands rather than environmental mandates. Spending on data centers accounted for 92% of U.S. GDP growth in the first half of 2025, creating massive demand for energy-efficient solutions that reduce operational costs.
Entrepreneurs entering this sector should target energy efficiency rather than generation. The infrastructure for renewable generation is increasingly dominated by utilities and large corporates, but optimization, storage, and management remain fragmented. Energy management systems that reduce consumption through automation and AI deliver immediate cost savings with measurable ROI, making sales cycles shorter than generation projects.
The regulatory environment adds urgency. Chief Sustainability Officers are evolving from compliance-centric to efficiency-centric roles, targeting energy management and IT automation that improve profit margins. This shift means sustainability budgets increasingly come from operations rather than CSR, putting decision-making closer to P&L responsibility and shortening approval processes.
Health, Wellness, and Preventive Technology
The global personalized medicine market is projected to grow from $88.21 billion in 2025 to $206.23 billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 11.2%. The opportunity extends beyond genomics to encompass mental health, preventive care, and integrated wellness platforms addressing chronic disease management.
The sector’s growth reflects demographic inevitability. Aging populations, rising chronic disease rates, and healthcare labor shortages create structural demand that transcends economic cycles. AI developments in healthcare enable smarter decisions, task automation, and unprecedented prediction accuracy, transforming diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care.
Entry points favor specialized solutions over broad platforms. Small businesses can focus on genetic testing or diagnostic tools for specific conditions, personalized nutrition and wellness programs tied to genomic insights, or partnerships with research institutions and hospitals. The key involves choosing narrow enough focus to develop genuine expertise while serving markets large enough to support venture-scale businesses.
Mental wellness presents particularly compelling opportunities. Digital therapeutics, AI-assisted therapy platforms, and workplace wellness solutions address massive unmet need with subscription business models and favorable unit economics. Remote delivery lowers customer acquisition costs while expanding addressable markets beyond major metros.
Preventive technology faces regulatory complexity but offers superior economics compared to treatment. Wearable devices providing real-time health monitoring enable proactive interventions that reduce long-term costs, aligning incentives across patients, providers, and payers. Entrepreneurs who navigate regulatory requirements gain defensible moats in markets with significant switching costs.
Digital and Immersive Experiences
The metaverse hype cycle has crashed, but the underlying technology finds practical applications in retail, education, and enterprise training. Augmented reality shopping experiences reduce return rates by helping customers visualize products before purchase. Virtual training simulations provide safe, scalable environments for high-risk industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
Generative AI systems capable of creating text, images, and videos will become cornerstones of digital content creation by 2026, enabling businesses to produce high-quality, customized content at scale. The revolution affects marketing, entertainment, and education simultaneously. Brands create immersive virtual experiences for customers, educators design personalized learning modules, and filmmakers leverage AI for visual effects and scriptwriting.
The business model shift matters more than the technology. Rather than building consumer metaverse platforms, successful ventures enable existing businesses to incorporate immersive elements into established workflows. A furniture retailer implementing AR room visualization generates immediate sales lift. A university deploying VR labs expands capacity without physical construction.
Education technology deserves specific attention. Demand for digital curriculum content, corporate upskilling programs, gamified learning, and hybrid learning infrastructure is expected to increase. The rise in remote learning offers opportunities to launch scalable businesses with relatively low entry barriers, particularly for industry-specific solutions, vocational training tools, or AI-powered tutoring.
Subscription, On-Demand, and Platform Services
The subscription economy matured beyond software into physical goods, services, and experiences. Recurring revenue models provide predictable cash flow and higher valuations compared to transactional businesses. Entrepreneurs can embed finance tools in existing e-commerce or gig economy platforms, develop niche compliance solutions, or create fraud prevention and cross-border payment services.
The global fintech market saw $44.7 billion in investment during H1 2025, with growing focus on AI-enabled applications. While fintech faces regulatory complexity, niche solutions addressing specific pain points, invoicing for freelancers, expense management for small businesses, embedded insurance, generate rapid adoption with lower regulatory burden than consumer banking.
Platform businesses connecting underutilized resources to demand continue demonstrating strong unit economics. The key involves finding fragmented supply and latent demand that existing platforms don’t serve efficiently. Vertical-specific marketplaces outperform horizontal platforms by understanding industry nuances and building specialized features that generic solutions lack.
On-demand services expanded beyond rides and food delivery into professional services, healthcare, and home maintenance. The model works when supply constraints (finding qualified providers) create friction that platforms can solve through vetting, scheduling, and payment processing. Success requires network effects where more providers attract more customers in self-reinforcing loops.
Navigating Sector Selection
Choosing the right sector involves assessing personal strengths against market dynamics. The fastest growing industries include AI & Automation, Renewable Energy, Fintech, Healthcare & Biotechnology, E-Commerce, Space & Advanced Manufacturing, and the Digital Experience Economy, but not all offer equal accessibility to bootstrapped founders or first-time entrepreneurs.
Capital intensity matters. AI services and fintech require less upfront investment than hardware or renewable energy generation. Regulatory burden affects time-to-market, healthcare and financial services face longer approval processes than pure software plays. Customer acquisition costs vary dramatically across sectors, with enterprise sales requiring different skills than consumer marketing.
The ideal sector aligns founder expertise with market timing and accessible entry points. An engineer with machine learning background has natural advantages in AI automation. A healthcare professional understands clinical workflows that technologists miss. A former teacher grasps educational pain points invisible to pure entrepreneurs.
Timing considerations extend beyond simple “early” or “late” assessments. Some sectors face near-term headwinds despite long-term promise. Today generative AI itself is wildly unprofitable, with companies needing to charge users far more than current pricing to recoup infrastructure costs. Entrepreneurs entering now must either offer dramatically superior economics or target markets willing to pay premium prices for genuine value.
The five sectors outlined above demonstrate unusual alignment: strong tailwinds, proven customer demand, accessible entry points, and realistic paths to profitability. They’re not the only opportunities, niche markets and emerging technologies always create outlier successes, but they offer the highest probability of building sustainable, venture-scale businesses in the year ahead. For entrepreneurs planning 2026 launches, understanding where structural growth concentrates provides the foundation for everything that follows.
Related: This article is part of Mooloo’s Business & Entrepreneurship Hub, covering how businesses are started, financed, scaled, and protected over time.