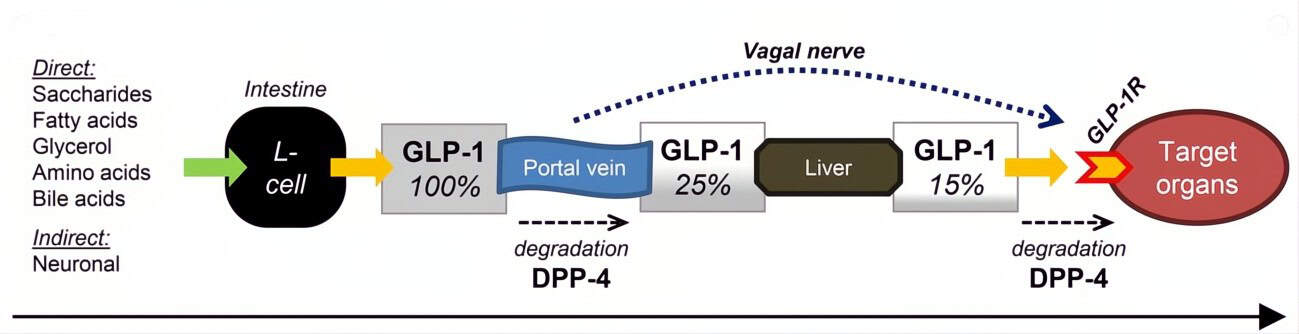
The $7B Acquisition That Just Changed Everything in Weight Loss Investing
5.1 min read
Updated: Dec 20, 2025 - 13:12:05
ADVERTISEMENT
Advertise with Us
ADVERTISEMENT
Advertise with Us
Related Posts
Other News
ADVERTISEMENT
Advertise with Us
Tags
Business & Entrepreneurship (80)
Crypto & Digital Assets (11)
Crypto As An Asset (3)
Custody Models (9)
How To & Guides (2)
Infrastructure and Access (11)
Investing (94)
Law & Control (49)
Loans & Credit (64)
Market Structure (18)
News (24)
Opinion (1)
Personal Finance (136)
Press Releases (4)
Regulation & RIsk (1)
Retirement (38)
Self Custody (12)
Tax Strategy (24)
Third Party Custody (72)
Why Custody Fails (27)