AI for Small Businesses: A Beginner-to-Intermediate Integration Roadmap for Established Companies
6.7 min read
Updated: Dec 21, 2025 - 09:12:41
Artificial intelligence has evolved from a big-corporate advantage into an essential productivity tool for small and mid-sized businesses. In 2025, AI helps firms streamline marketing, automate operations, and reduce costs without needing proprietary systems. The key is phased, strategic adoption, starting with quick wins, training teams, and scaling responsibly with compliance and measurable ROI in mind.
- AI adoption is mainstream: 42% of companies use AI and another 40% are piloting it, per the IBM Global AI Adoption Index 2023.
- Start with high-impact tasks: Automate customer communication, invoicing, and content creation for early ROI.
- Use ready-made tools: Platforms like HubSpot, ChatGPT, and Zapier deliver fast efficiency gains without technical expertise.
- Invest in staff training: 34% of firms cite skill gaps as the main adoption barrier, internal workshops build consistency and confidence.
- Prioritize compliance and metrics: Follow FTC and SBA guidance on responsible data use, and measure outcomes to sustain long-term gains.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has shifted from being a niche innovation confined to major corporations into a mainstream business tool that even small and mid-sized firms are embracing. Today, AI adoption is not limited to cutting-edge tech startups, it is becoming essential for established small businesses seeking to stay competitive, improve efficiency, and manage costs in a challenging economic environment.
By deploying AI carefully and strategically, these businesses can enhance productivity, streamline operations, and create sustainable growth opportunities. This detailed roadmap is designed to help established small business owners understand not only how AI can be integrated into daily operations, but also how to avoid common pitfalls while ensuring compliance, scalability, and long-term impact.
The Current Landscape: Why Small Businesses Are Turning to AI
AI adoption has accelerated dramatically in the past three years. According to the IBM Global AI Adoption Index 2023, 42% of companies are actively using AI, while another 40% are in the planning or pilot stage.
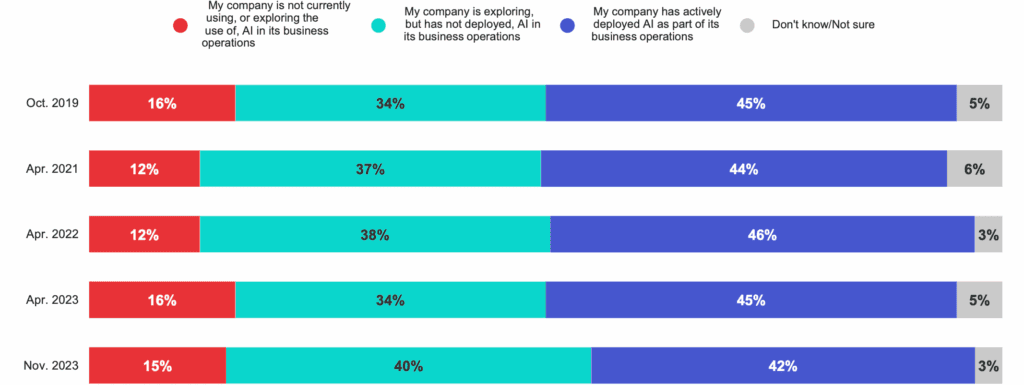
Source: IBM
Similarly, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce Technology Engagement Center reports that nearly one in four small businesses in the U.S. has already implemented AI in some capacity, whether for customer support, marketing, or internal operations.
Industry reports highlight that small businesses are not experimenting with AI in isolation, they are adopting ready-made, user-friendly tools. Salesforce’s Small & Medium Business Trends Report indicates that the most common AI applications include:
-
Customer relationship management (CRM) automation to streamline lead handling and sales pipelines
-
Marketing personalization and AI-assisted content creation to improve engagement
-
Customer service chatbots to handle inquiries at scale without increasing headcount
-
Back-office process automation such as invoicing, scheduling, and document handling
These are not speculative technologies, they are proven tools that deliver measurable results without requiring businesses to build proprietary AI systems.
Phase One: Awareness and Opportunity Mapping
Before purchasing any AI platform, businesses must first evaluate where AI can deliver tangible value. The goal is not to chase trends but to identify repetitive, rules-based, or data-heavy tasks that consume time without adding proportionate value.
High-impact areas often include:
-
Customer communication: Using chatbots or automated responders to reduce wait times.
-
Marketing & content: Generating blog posts, social media updates, or product descriptions with generative AI.
-
Operations: Automating payroll, invoicing, and compliance reporting.
-
Sales: AI-driven lead scoring, pipeline prioritization, and follow-up automation.
-
HR & recruitment: Screening applicants, drafting job postings, and automating onboarding workflows.
A McKinsey & Company survey found that small businesses achieve the highest ROI when AI is applied to marketing, customer service, and supply-chain optimization. This insight reinforces the importance of starting with functions directly tied to revenue and efficiency.
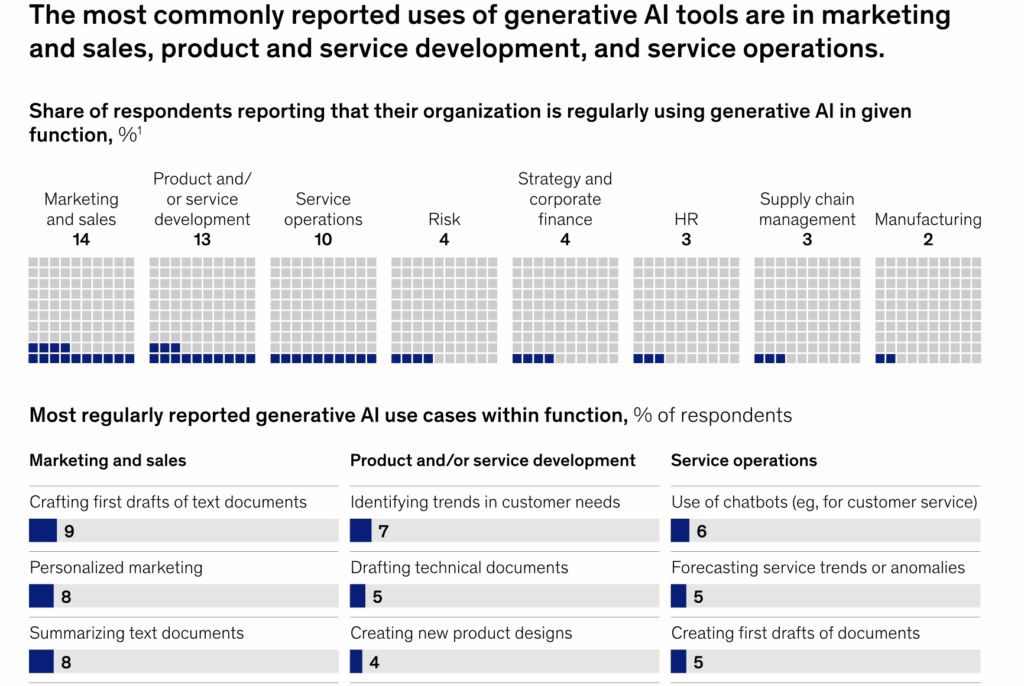
Source: McKinsey & Company
Phase Two: First Tools and Easy Wins
Once high-value opportunities are mapped, businesses should adopt low-barrier, cost-effective AI tools that require minimal setup. At this stage, the objective is to demonstrate fast, measurable improvements.
Examples include:
-
Generative AI assistants (e.g., ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Microsoft CoPilot) for creating content, summarizing reports, or drafting communications.
-
CRM automation (e.g., HubSpot, Zoho CRM) to personalize customer journeys, automate outreach, and analyze engagement.
-
AI scheduling & productivity tools (e.g., Google Workspace Smart Compose, Calendly AI) to cut down on manual coordination.
-
Workflow automation platforms (e.g., Zapier, Make) that integrate AI modules to streamline cross-platform tasks.
Quick wins may include cutting content production time in half, reducing customer inquiry response times from hours to minutes, or automating entire segments of routine administrative tasks. These results not only justify AI adoption but also build internal confidence.
Phase Three: Workflow Integration and Staff Enablement
Once the initial tools prove valuable, the next step is to deepen integration by embedding AI into core business workflows rather than treating it as a separate layer.
Key elements of this phase:
-
Training staff to use AI effectively, not just management. According to the IBM index, lack of skills is a top barrier to adoption for 34% of companies. Internal workshops and shared prompt libraries can help staff use generative tools consistently.
-
Automating multi-step processes. For example, leads captured on a website can trigger AI-based enrichment, scoring, CRM entry, and automated follow-up, all without manual input.
-
Integrating AI with analytics to improve decision-making, such as predictive sales forecasting or inventory optimization.
At this stage, businesses often begin to see compound efficiency gains as AI reduces delays and human error across multiple departments.
Phase Four: Scaling and Strategic Integration
The final stage is to move from experimentation to strategic integration, where AI becomes part of the business model rather than a series of tactical add-ons.
Strategic integration typically involves:
-
Selecting a core AI platform or ecosystem that aligns with your tech stack (e.g., Microsoft Copilot if using Microsoft 365, or Salesforce Einstein for CRM-heavy operations).
-
Setting clear KPIs to measure AI impact on costs, productivity, customer satisfaction, or revenue.
-
Regularly reviewing legal and compliance obligations, including data privacy and security, which are increasingly regulated. The U.S. Small Business Administration and FTC offer guidance on responsible data use.
-
Updating workflows and job descriptions to reflect new capabilities rather than simply layering tools on top of old processes.
According to McKinsey’s 2023 State of AI report, companies that successfully scale AI typically focus on governance, change management, and consistent measurement rather than chasing the latest technologies.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Many businesses fail not because AI technology underperforms, but because its implementation is poorly executed. Common missteps include purchasing tools without first mapping them to actual business needs, neglecting staff training which leads to low adoption, ignoring compliance requirements that create legal and reputational risks, and failing to measure results, making it difficult to justify continued investment. To avoid these pitfalls, businesses need to follow a disciplined, step-by-step roadmap where each phase builds logically on the last.
Key Takeaways
-
AI adoption among small businesses is growing steadily, with proven use cases in marketing, customer service, operations, and administration.
-
A phased integration roadmap allows established businesses to adopt AI incrementally and strategically, minimizing risk.
-
Early wins come from off-the-shelf tools that require little technical expertise but deliver measurable efficiency gains.
-
Successful scaling depends on training, workflow integration, compliance, and clear performance metrics, not chasing hype.
-
With the right approach, AI can deliver meaningful productivity and competitive advantages to established small businesses without major upfront investment.
Final Word
AI is no longer a futuristic add-on, it is becoming a core operational tool for businesses of all sizes. Established small businesses are uniquely positioned to benefit, as they already have customer relationships, institutional knowledge, and proven workflows that AI can enhance.
When implemented thoughtfully, AI reduces costs, saves time, and improves decision-making. More importantly, it helps level the playing field, allowing small businesses to compete with larger rivals that historically had access to greater resources.
For business owners ready to take the next step, the journey begins not with technology itself, but with a clear understanding of where AI creates the most value. By layering AI intelligently onto existing strengths, small businesses can unlock sustainable growth and build resilience in an increasingly competitive marketplace.